NVIDIA Researchers Introduce KVTC Transcoding Pipeline to Compress Key-Value Caches by 20x for Efficient LLM Performance
Running Large Language Models (LLMs) at scale is a major engineering challenge due to the management of the Key-Value (KV) repository. As models grow in size and processing power, KV’s cache footprint grows and becomes a major bottleneck in throughput and performance. In modern Transformers, this cache can take many gigabytes.
NVIDIA researchers presented KVTC (KV Cache Transform Coding). This lightweight conversion code compresses KV caches for compact on-GPU and off-GPU storage. It reaches up to 20x compression while maintaining the logic and accuracy of long content. In certain cases of use, it can reach 40x or more.
The Memory Dilemma in LLM Inference
In production, indexing frameworks treat the local KV repository as a database. Techniques such as shared start-up encourage cache reuse to speed up responses. However, classic caches use scarce GPU memory. Developers are currently faced with a difficult choice:
- Back up: Takes memory needed by other users.
- Dump cache: It involves high recalculation costs.
- Load the archive: It moves data to CPU DRAM or SSDs, resulting in higher throughput.
KVTC greatly reduces this problem by lowering the on-chip storage cost and reducing the bandwidth required for loading.


How KVTC Pipe Works?
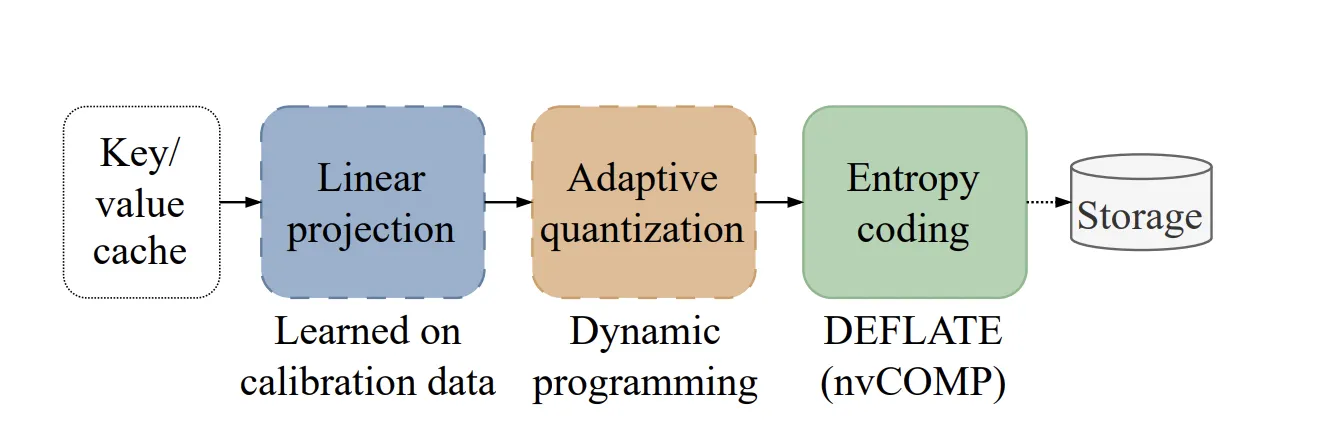
The method is inspired by classical media compression. A learned orthonormal transformation is applied, followed by dynamic estimation and entropy coding.
1. Component Analysis (PCA)
Different attention heads tend to show similar patterns and a high degree of correlation. KVTC uses Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to classify features linearly. Unlike other methods that calculate different decays every time, KVTC calculates the PCA basis matrix V and in the measurement dataset. This matrix is then reused in all future caches during the decision process.
2. Adaptive Quantization
The system uses PCA ordering to allocate a fixed budget to all links. High diversity components get more bits, while others get fewer. KVTC it uses a dynamic programming (DP) algorithm to find the correct bit assignment that minimizes the reconstruction error. Most importantly, DP tends to allocate 0 bits in tracking key components, allowing for early size reduction and faster operation.
3. Entropy code
The measured signals are packed and compressed using i DEFLATE algorithm. To maintain speed, KVTC uses i nvCOMP library, which enables parallel compression and decompression directly on the GPU.
Securing Valuable Tokens
Not all tokens are pressed equally. KVTC avoids pressing two specific types of tokens because they offer inconsistent attention accuracy:
- Attention Sinks: I 4 oldest tokens respectively.
- Sliding Window: I 128 the most recent tokens.
Ablation studies show that compressing these specific tokens can significantly reduce or destroy accuracy at high compression rates..
Ratings and Success
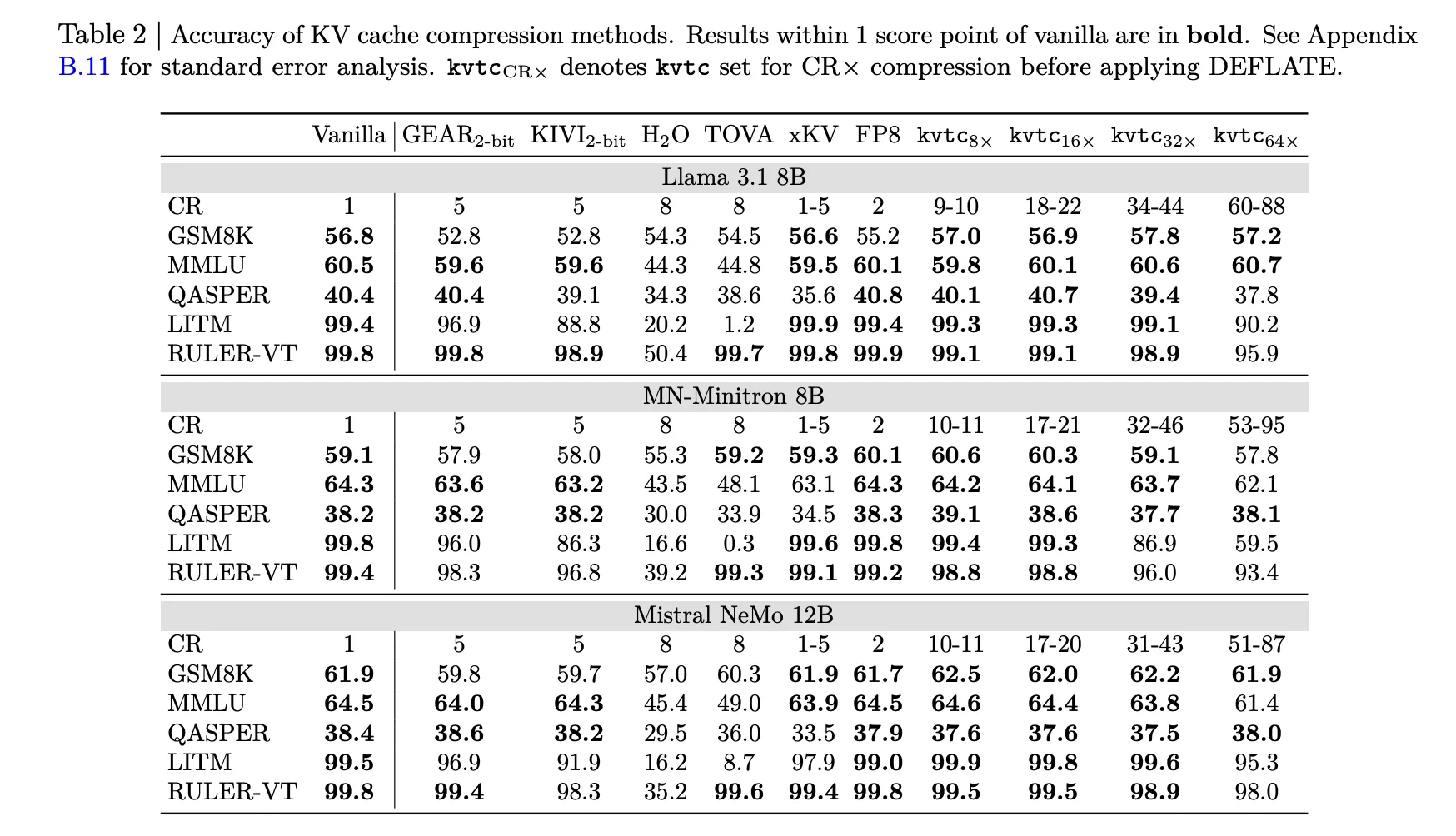
A team of researchers checked KVTC with models like Llama-3.1, Mistral-NeMo, and R1-Qwen-2.5.
- Accuracy: In 16x pressure (approx 20x after DEFLATE), the model always stores the results internally 1 points points for vanilla models.
- TTFT reduction: for 8K core length, kvtc can reduce Time-To-First-Token (TTFT) by arrival 8x compared to full rework.
- Speed: The measurement is fast; with the 12B model, it can be finished inside 10 minutes on NVIDIA H100 GPU.
- Storage Max: The additional data stored for each model is small, representative only 2.4% of parameters of the model Llama-3.3-70B.
KVTC is an efficient architecture for running memory-efficient LLM. It does not change the model weights and is directly compatible with other tokenization methods.

Key Takeaways
- High Compression with Low Accuracy Loss: KVTC reaches the level 20x compression ratio while keeping the results internal 1 score point of vanilla (uncompressed) models across most benchmarks and long-term context.
- Change the Encoding Pipeline: The method uses a pipeline inspired by classical media compression, combining PCA-based feature classification, adaptive quantization with a dynamic system, and lossless entropy encoding (DEFLATE).
- Key Token Protection: To maintain the functionality of the models, KVTC avoid stress i 4 the old tokens of the ‘attention sink’ and the ‘sliding window’ of 128 the most recent tokens.
- Working Effectively: The system is ‘untuned,’ requiring only a short initial calibration (below 10 minutes in the 12B model) which leaves the model parameters unchanged and adds a little extra storage—only 2.4% for the 70B model.
- Significant Latency Reduction: By reducing the amount of data stored and transmitted, KVTC can reduce Time-To-First-Token (TTFT) by arrival 8x compared to full recalculation of KV buffers for long conditions.
Check out Paper here. Also, feel free to follow us Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to Our newspaper. Wait! are you on telegram? now you can join us on telegram too.